
Artificial Intelligence has moved from buzzword to backbone. It dominates headlines, moves markets, and is reshaping the future of technology and the economy. For most people, AI is already part of daily life, and its influence will only deepen. For equity markets the question is not whether AI matters but where the next wave of opportunity lies. The dominant players such as Meta, Microsoft, Alphabet, and Amazon remain at the center of the trade, powering the buildout of large language models, machine learning, and the broader “intelligence revolution”. These firms are projected to invest more than $300 billion in AI related capital expenditures over the next year, with that figure on pace to approach $1 trillion annually by 2030.
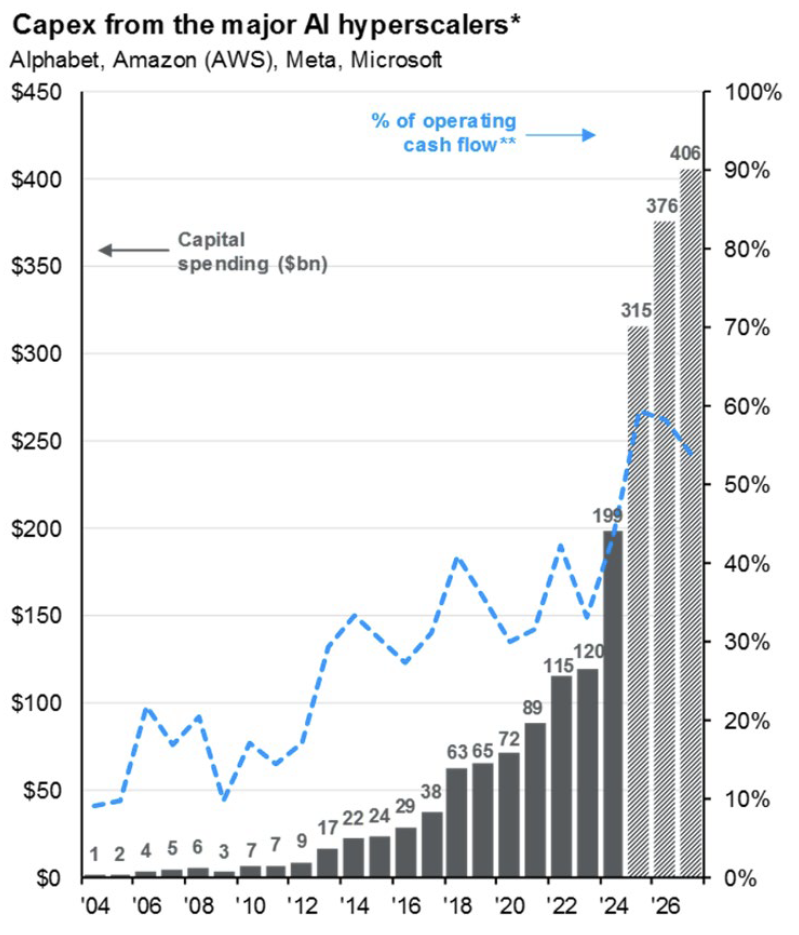
The economic footprint is already significant. According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, AI spending has now surpassed consumer spending as a driver of U.S. GDP growth. While much of this capital is flowing to the tech giants, which collectively still account for nearly 40% of the S&P 500, the ripple effects extend far beyond the index leaders. Sub industries positioned to supply, support, and scale AI adoption stand to benefit from one of the most powerful investment cycles in decades.
The Origins of AI
As I always like to do, let’s take a quick step back and set the stage. Britannica defines artificial intelligence as the ability for a digital computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent beings. Webster’s definition is nearly identical, with the added point that the computer system uses machine learning techniques applied to large collections of data.
Using these definitions, if someone were to say that the bull markets of 2023 and 2024 were attributed to the “creation” of AI, they would only be half right. The beginnings of AI stretch back to mathematics and logic research in the 1940s and 1950s when Alan Turing released works such as Computing Machinery and Intelligence. He posed the pivotal question “Can machines think?”. Initially, many dismissed him as crazy, which has often been the fate of scientific pioneers.
A key milestone came in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, where the term artificial intelligence was officially coined. The highlight of the event was a demonstration called the “Logic Theorist” developed by Allen Newell, Herbert Simon, and Cliff Shaw, which mimicked the problem-solving skills of a human mathematician. This was the true beginning of AI as we understand it today.
While the history of AI is fascinating, it’s not the point of this article. The point of this article is to identify what comes after the meteoric rise of 2023 and 2024 in equity markets. These outsized gains were driven by the release and rapid adoption of generative AI programs like ChatGPT. Generative AI revealed to the general public just how powerful AI could be in a practical and accessible way. It fueled expectations of a massive productivity boom, triggered a wave of corporate investment, and pushed investors to seek exposure to the companies best positioned to capture this opportunity.
At the center of this trade were the mega cap names that investors know well. Nvidia, Amazon, Alphabet, Microsoft, and Meta established early dominance in AI infrastructure and deployment, leading the S&P 500 to strong gains. The first wave of enthusiasm has been concentrated in a handful of dominant companies, but the broader story is only beginning to unfold. The technology is moving beyond chipmakers and major platforms, and into the businesses that provide the infrastructure, tools, and applications that make AI usable at scale. Identifying these adjacent beneficiaries is critical, as they represent the next layer of growth opportunities beyond the early winners.
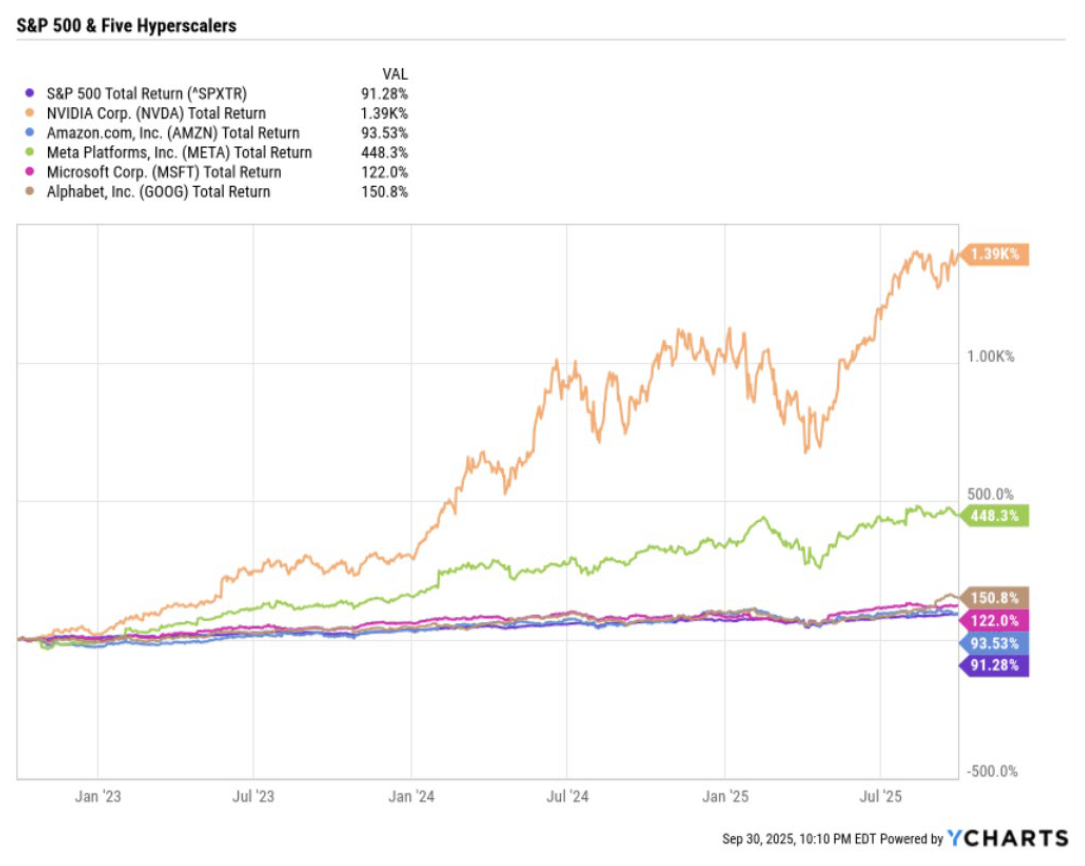
The Broader Ecosystem
Highlighted below are six industries within the broader AI ecosystem that stand to benefit as adoption accelerates. These areas extend past the familiar Magnificent 7 and provide a clearer view of where the next wave of growth may emerge.
Software, IT, and Cybersecurity
For AI to move from concept to daily business utility, it requires strong software frameworks, reliable IT infrastructure, and resilient cybersecurity. These elements provide the structure that allows new applications to run smoothly, scale effectively, and remain secure.
Several companies are already at the forefront. Atlassian Corporation provides collaboration and workflow software that helps teams manage AI-driven projects and operations. Okta provides identity and access management solutions that secure authentication and protect sensitive data in increasingly complex digital environments. SAP integrates AI into enterprise resource planning software, enhancing decision making across supply chains, finance, and customer engagement.
The companies that enable this secure and seamless integration will be critical in shaping the next stage of AI deployment, capturing growth as organizations embed the technology more deeply across operations.
AI Infrastructure, Utilities, Nuclear
AI applications are notoriously energy and data intensive, driving growing demand for computing infrastructure and reliable utility support. Data centers, cloud services, and power generation form the physical backbone that enables AI to operate at scale, making this sector a critical enabler of broader AI deployment.
Companies operating in this space include Vertiv Holdings, which designs, manufacturers, and services equipment that manages power and cooling for data centers. Vistra Corporation delivers electricity and natural gas to residential, commercial, and industrial customers across the United States. In the nuclear sector, Cameco and Uranium Energy supply fuel that supports large scale, low carbon power generation. Powell industries and Constellation Energy Corp provide power and energy distribution along with electrical equipment for data center operations and energy intensive AI workloads.
Looking forward, firms that provide resilient, scalable, and low carbon infrastructure will be central as AI workloads grow. With low operational costs and powerplant lifespans often exceeding 80 years, nuclear energy in particular offers a unique convergence of sustainability and capacity, highlighting the intersection of energy demand and the foundational systems that support AI.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing applies the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in ways that classical computers cannot. Unlike traditional bits, which are either 0 or 1, quantum bits (qubits) can exist in multiple states simultaneously, allowing certain calculations to be performed exponentially faster. While the technology remains in its early stages and faces challenges such as scalability and error rates, its potential is significant.
Companies active in this industry include D-Wave which focuses on quantum annealing, a method designed to tackle complex optimization problems, and Rigetti Computing, which is developing gate-based quantum systems that aim for broader applications.
Quantum computing has the potential to enable breakthroughs across multiple industries. In biotech, it could simulate complex molecular interactions for drug discovery. In finance, it could enhance portfolio optimization and risk modeling. In cybersecurity, it could reshape encryption standards. For AI, quantum machines could accelerate model training and solve problems beyond the reach of even the most advanced supercomputers. Quantum represents a longer-term frontier with the potential to dramatically expand AI capabilities as technology matures.
Biotechnology & Robotics
AI is transforming the life sciences and automation sectors by accelerating research, improving precision, and enabling smarter decision-making. In biotech, AI can model complex biological systems, streamline drug discovery, and support personalized medicine. In robotics, AI drives advanced automation in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, creating more efficient and adaptive systems.
Several companies are already harnessing this potential. Tempus AI applies AI to precision medicine, using data analytics to guide cancer care and optimize treatment decisions. Procept BioRobotics specializes in AI-driven surgical robotics, enhancing precision and outcomes in minimally invasive procedures. Exelixis Inc leverages AI in drug discovery and development, helping identify promising therapeutic candidates more efficiently.
The intersection of AI, biotech, and robotics is poised for rapid growth. Companies that combine automation, data analytics, and life sciences expertise will be well positioned to capitalize on the increasing demand for faster, smarter, and more efficient solutions in healthcare, research, and treatments.
Blockchain & Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies are increasingly intersecting with AI by providing secure, decentralized ways to store and manage data, execute transactions, and verify digital processes. Beyond their role as digital assets, these technologies offer infrastructure that can complement AI applications, particularly in areas requiring transparency, security, and distributed computation.
A number of companies are actively positioned in this space. Terawulf develops energy-efficient mining infrastructure for cryptocurrencies, supporting the broader blockchain ecosystem. Robinhood offers cryptocurrency trading and financial services that make digital assets more accessible to retail investors. MicroStrategy has adopted Bitcoin as a corporate treasury asset and is actively investing in blockchain related technologies to support its AI and analytics strategies.
As AI adoption expands, blockchain and cryptocurrencies will play a key role in enabling secure, decentralized frameworks for data sharing, computation, and transactions. Companies that integrate AI with blockchain infrastructure or leverage digital assets strategically are likely to benefit from the growing convergence of these technologies across finance, enterprise, and emerging digital platforms.
The Next Wave of AI
Together, these six industries illustrate the breadth of AI’s influence beyond the first group of dominant names. From software and cybersecurity to quantum computing, biotech, blockchain, and energy infrastructure, AI is shaping both digital and physical domains in ways that redefine business and innovation. Each area represents unique opportunities, whether by enabling adoption, providing the backbone of infrastructure, or unlocking new capabilities.
As AI becomes more deeply embedded in the global economy and financial markets, investors and businesses that look beyond the headline leaders will be better prepared to capture the next growth opportunities. The early winners proved the promise of AI, but the sectors building around them will determine how durable and far reaching that promise becomes.
Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it. I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Investment advice offered through Great Valley Advisor Group (GVA), a Registered Investment Advisor. I am solely an investment advisor representative of Great Valley Advisor Group, and not affiliated with LPL Financial. Any opinions or views expressed by me are not those of LPL Financial. This is not intended to be used as tax or legal advice. All performance referenced is historical and is no guarantee of future results. All indices are unmanaged and may not be invested into directly. Please consult a tax or legal professional for specific information and advice.
LPL Compliance Tracking #: 805096
